120 - How to add RedHat Install ISOs to Easy2Boot
This Tutorial assumes you have already made a working Easy2Boot (E2B) multiboot USB drive.
If you are using a FAT32 E2B USB drive:
Method 1 - FAT32
If you have a FAT32 formatted Easy2Boot USB drive, simply use the RedHat.mnu file which you can find in the \_ISO\docs\Sample mnu Files folder on the E2B drive.
1. Copy the RedHat.mnu file to the \_ISO\MAINMENU\MNU folder (or \_ISO\LINUX\MNU)
2. Copy the RedHat ISO file to the same folder
3. Edit the .mnu file so that the filename of the ISO file matches the ISO you are using.
If you are using an NTFS E2B USB drive:
Method 2 - NTFS+FAT32
1. Use Easeus Home Partition Master (free) or the Trial Pro version, to create a second Primary FAT32 partition on your NTFS Easy2Boot USB drive. The paritions should look like this:
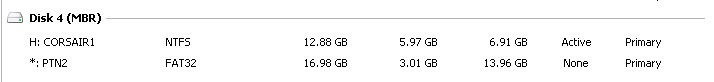
Note that there must ONLY be two Primary partitions. The volume names can be anything that you choose.
2. Copy the RedHat.mnu file to your desired folder (e.g. \_ISO\MAINMENU\MNU)
3. Use RMPrepUSB - Ctrl-O to swap Windows access to partition 2 (only required if you are using a USB Removable Flash drive)
4. Create an identical folder structure on the FAT32 partition to match the location of the .mnu file and copy the ISO file into that new folder - e.g.
PTN1 = NTFS /_ISO/MAINMENU/MNU contains .mnu file
PTN2 = FAT32 /_ISO/MAINMENU/MNU contains the iso file
5.Use RMPrepUSB - Ctrl-O to swap Windows access to partition 1 again (only required if you are using a USB Removable Flash drive)
6. Finally edit the RedHat.mnu file to use a matching .iso filename for the one you have placed on the FAT32 partition
Method 3 - NTFS+FAT32 Image
This method can be used if your E2B drive is NTFS (or FAT32 or ext2). It requires you to have a spare USB drive that you can format - this is used to create a partition image which we can use on the E2B drive. The spare drive is not required once the image has been made and can then be reformatted and used for other purposes.
1. Format a spare USB Flash/HDD as FAT32, 1 partition, SIZE=(size of Redhat ISO) + 100MB (e.g. if ISO is 3149MB, format USB flash drive as 3250) - Use RMPrepUSB for this. It will save space if you keep the size of the FAT32 partition as small as possible
2. Copy the redhat ISO onto the root of the FAT32 USB drive - do not extract the ISO, just copy the ISO file over. The FAT32 drive will now contain just one single redhat ISO file.
3. Use RMPrepUSB - Drive->File, Filename=REDHATPTN.IMG, start=P1, size=P1, filestart=0 to make an image of the FAT32 USB drive partition
4. Copy the file REDHATPTN.IMG to \_ISO\MAINMENU\MNU folder (or any \_ISO\xxxxxx\MNU folder) on your E2B NTFS drive
5. Copy the file RedHat_NTFS.mnu from the \_ISO\docs\Sample mnu Files folder to \_ISO\MAINMENU\MNU folder (or any \_ISO\xxxxxx\MNU folder) on E2B NTFS drive
6. Change rhel-server-5.7-i386-dvd filename inside the .mnu file to match your ISO filename
See my blog post for more details.
Installing RedHat
1. When you run the RedHat ISO using any of the above methods, you will be prompted to choose the source of the packages to be installed:
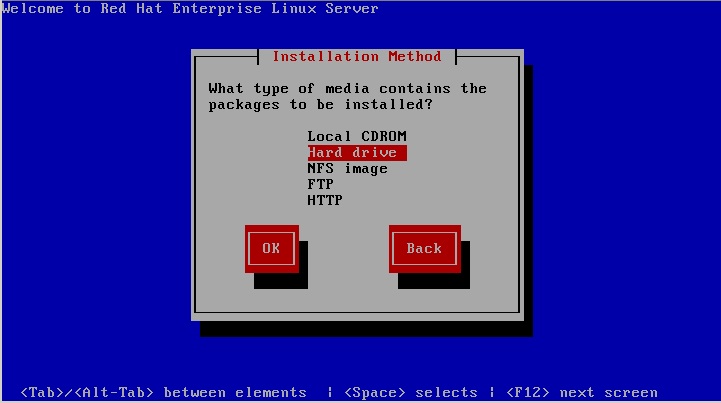
Choose Hard drive
Choose Hard drive
2. You will now be presented with a list of devices which will represent the drives found in the system. One of these will be your E2B USB drive.
hda will be the first internal IDE drive
sda will be the first internal SATA drive
sdb will be the 2nd internal hard drive (if present) or the E2B USB drive (if not 2nd internal drive is present)
If you have only one internal SATA drive, then sdb will be your E2B USB drive (assuming the internal drive is a SATA drive).
e.g. /dev/sdb1 might be the first primary partition on the E2B USB drive, /dev/sdb4 might be the 4th primary partition on the E2B USB drive.
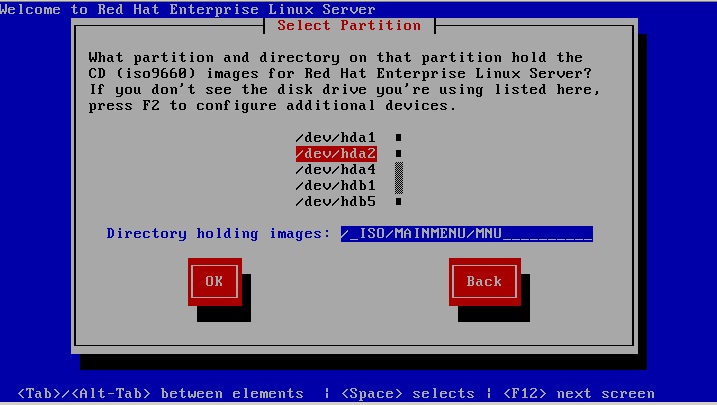
Assuming you have identified your E2B USB drive as device /dev/sdb ...
If using Method 1 - choose /dev/sdb1 and enter the correct path for the ISO file - e.g. /_ISO/MAINMENU/MNU
If using Method 2 - choose /dev/sdb2 and enter the correct path for the ISO file - e.g. /_ISO/MAINMENU/MNU
If using Method 3 - choose /dev/sdb4 - the path can be left empty or use /
You can now proceed to install RedHat linux to your internal USB hard disk.


